A pilonidal cyst is a small sac that forms in the skin, typically located near the tailbone at the top of the cleft of the buttocks. This cyst can be filled with hair, skin debris, and other bodily fluids, leading to discomfort and potential complications. We often find that these cysts are more common in young adults, particularly those who are sedentary or have a family history of similar issues.
The term “pilonidal” itself derives from Latin, meaning “hair nest,” which aptly describes the nature of these cysts as they often contain hair follicles. Pilonidal cysts can vary in size and may remain asymptomatic for long periods.
However, they can become inflamed or infected, leading to significant pain and discomfort.
In some cases, we may notice that these cysts can develop into abscesses, which are painful collections of pus that require medical attention. Understanding what a pilonidal cyst is helps us recognize its potential impact on our health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- A pilonidal cyst is a small sac filled with debris and hair that forms near the top of the buttocks.
- Symptoms of pilonidal cysts include pain, swelling, redness, and drainage of pus or blood.
- Pilonidal cysts are caused by ingrown hairs, friction, and trauma to the area.
- Risk factors for pilonidal cysts include obesity, excess body hair, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Diagnosis of pilonidal cysts is usually based on physical examination and medical history, but imaging tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Symptoms of Pilonidal Cysts
The symptoms of pilonidal cysts can range from mild to severe, depending on whether the cyst is infected or inflamed. Initially, we might not experience any symptoms at all; however, as the condition progresses, we may notice swelling and tenderness in the area around the cyst. This discomfort can make sitting or standing for extended periods quite challenging.
In some instances, we may also observe redness and warmth around the cyst, indicating inflammation. If the pilonidal cyst becomes infected, we may experience more pronounced symptoms such as increased pain, drainage of pus or blood from the cyst, and even fever. The presence of these symptoms often signals that medical intervention is necessary.
It’s crucial for us to pay attention to these signs, as they can help us determine the appropriate course of action to alleviate our discomfort and prevent further complications.
Causes of Pilonidal Cysts

The exact cause of pilonidal cysts remains somewhat unclear, but several factors contribute to their development. One primary theory suggests that they arise from hair follicles becoming clogged with hair and skin debris. When this blockage occurs, it can lead to the formation of a cyst beneath the skin.
We often find that individuals with coarse or thick body hair are more susceptible to developing these cysts due to the increased likelihood of hair penetrating the skin. Another contributing factor is friction or pressure on the area, which can occur from prolonged sitting or activities that put stress on the tailbone region. For instance, those who spend long hours sitting at a desk or driving may be at a higher risk.
Additionally, we should consider that genetics may play a role; if someone in our family has experienced pilonidal cysts, we might be more prone to developing them ourselves.
Risk Factors for Pilonidal Cysts
Several risk factors can increase our likelihood of developing pilonidal cysts. As mentioned earlier, age is a significant factor; these cysts are most commonly seen in individuals between the ages of 15 and 35. Additionally, gender plays a role, as men are more likely than women to develop pilonidal cysts.
This disparity may be attributed to differences in body hair distribution and hormonal factors. Obesity is another risk factor that we should be aware of. Excess weight can lead to increased friction in the tailbone area and make it more challenging for us to maintain proper hygiene.
Furthermore, individuals with a sedentary lifestyle are at greater risk due to prolonged pressure on the area. Understanding these risk factors allows us to take proactive measures in managing our health and reducing our chances of developing pilonidal cysts.
Diagnosis of Pilonidal Cysts
Diagnosing a pilonidal cyst typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. During this examination, we can expect the doctor to assess the area around the tailbone for signs of swelling, redness, or drainage. In most cases, a visual inspection is sufficient for diagnosis; however, if there are concerns about infection or complications, additional tests such as imaging studies may be ordered.
In some instances, we may also be asked about our medical history and any symptoms we have been experiencing. This information helps the healthcare provider determine whether the cyst is likely to be causing our discomfort or if there are other underlying issues at play. By understanding the diagnostic process, we can better prepare ourselves for our medical appointments and ensure that we receive appropriate care.
Complications of Pilonidal Cysts
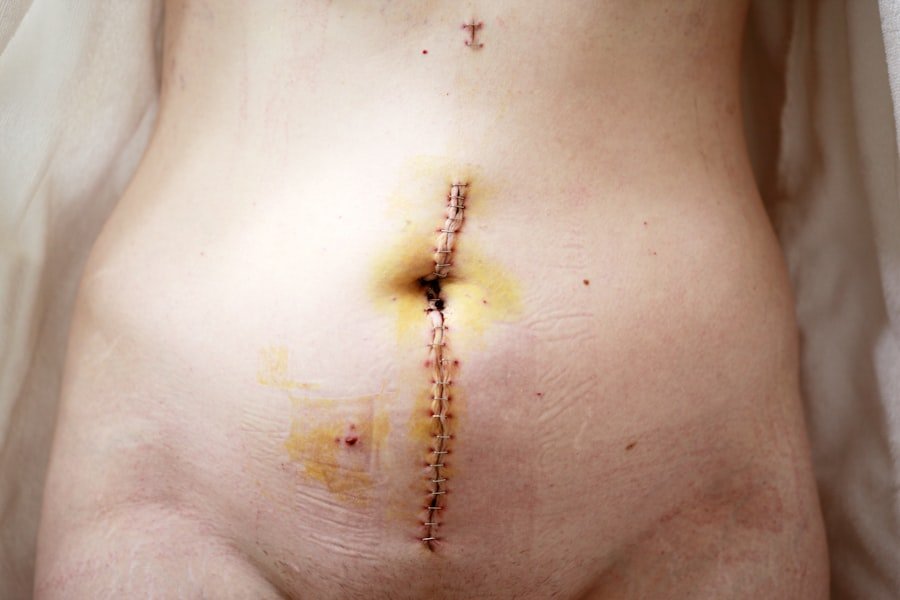
While many pilonidal cysts remain asymptomatic and do not lead to complications, there are instances where they can become problematic. One of the most common complications is infection, which can result in an abscess forming around the cyst. This condition can cause significant pain and may require drainage by a healthcare professional.
If left untreated, an infected pilonidal cyst can lead to further complications such as cellulitis or systemic infections. Another potential complication is chronic pilonidal disease, where the cyst becomes recurrent and leads to ongoing discomfort and inflammation. In such cases, we may find ourselves dealing with multiple flare-ups over time, which can significantly impact our quality of life.
Recognizing these potential complications early on allows us to seek timely medical intervention and minimize any adverse effects on our health.
Treatment Options for Pilonidal Cysts
When it comes to treating pilonidal cysts, several options are available depending on the severity of our symptoms and whether an infection is present. For mild cases without infection, conservative management may be sufficient. This approach often includes maintaining proper hygiene in the affected area and using warm compresses to alleviate discomfort.
If an infection is present or if the cyst is causing significant pain, we may require more aggressive treatment options such as antibiotics or drainage procedures. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the cyst entirely. This decision typically depends on factors such as the frequency of flare-ups and our overall health status.
By understanding these treatment options, we can work collaboratively with our healthcare providers to determine the best course of action for our individual needs.
Home Remedies for Pilonidal Cysts
While medical treatment is often necessary for pilonidal cysts, there are several home remedies that we can consider to help manage mild symptoms and promote healing. One effective approach is maintaining good hygiene in the affected area by keeping it clean and dry. Regularly washing with mild soap and water can help prevent infection and reduce irritation.
We might also find relief through warm compresses applied to the area several times a day. The heat can help soothe inflammation and promote drainage if there is any pus present. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate discomfort while we wait for further medical evaluation or treatment.
While these home remedies can provide temporary relief, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Surgical Procedures for Pilonidal Cysts
In cases where conservative treatments fail or if we experience recurrent pilonidal cysts, surgical intervention may become necessary. There are several surgical options available depending on the complexity of our condition. One common procedure is incision and drainage, where the healthcare provider makes an incision in the cyst to allow any trapped fluid or pus to escape.
For more extensive cases, we may require excision surgery, where the entire cyst and surrounding tissue are removed. This procedure aims to eliminate any potential for recurrence by addressing the root cause of the problem. After surgery, proper wound care is crucial for promoting healing and preventing infection.
Understanding these surgical options empowers us to make informed decisions about our treatment plan in collaboration with our healthcare team.
Prevention of Pilonidal Cysts
Preventing pilonidal cysts involves adopting certain lifestyle habits that minimize our risk factors. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly reduce pressure on the tailbone area and improve overall hygiene. We should also aim to keep the area clean and dry by showering regularly and using talcum powder if necessary to absorb moisture.
Additionally, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting can help decrease friction in the area where pilonidal cysts typically form. If our jobs require long hours at a desk or driving, taking regular breaks to stand up and move around can be beneficial. By implementing these preventive measures into our daily routines, we can significantly lower our chances of developing pilonidal cysts.
When to See a Doctor for Pilonidal Cysts
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for pilonidal cysts is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring effective treatment. If we notice any signs of infection—such as increased redness, swelling, warmth around the cyst, or drainage of pus—it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Additionally, if we experience persistent pain or discomfort that interferes with our daily activities, seeking medical advice is warranted.
Even if we have previously been diagnosed with a pilonidal cyst but notice changes in symptoms or an increase in frequency of flare-ups, it’s wise to revisit our healthcare provider for further evaluation. Early intervention can help us avoid more severe complications down the line and ensure that we receive appropriate care tailored to our specific needs. In conclusion, understanding pilonidal cysts—ranging from their definition and symptoms to treatment options—empowers us to take charge of our health effectively.
By recognizing risk factors and implementing preventive measures, we can work towards minimizing our chances of developing these uncomfortable conditions while ensuring timely medical intervention when necessary.
If you are interested in learning more about skin conditions, you may want to check out this article on acne. Acne is a common skin condition that affects many people, and understanding its causes and treatment options can be helpful. Additionally, if you are looking for a comprehensive guide on hair removal, you may want to read this article on black wax hair removal. These articles provide valuable information on different skin and hair-related topics that may interest you.
FAQs
What are pilonidal cysts?
Pilonidal cysts are small sacs filled with debris and hair that develop in the cleft at the top of the buttocks. They can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort.
What are the symptoms of pilonidal cysts?
Symptoms of pilonidal cysts may include pain, redness, swelling, and drainage of pus or blood from the cyst. Some individuals may also experience fever and discomfort when sitting or walking.
What causes pilonidal cysts?
Pilonidal cysts are often caused by ingrown hairs that penetrate the skin. Friction and pressure in the cleft of the buttocks can also contribute to the development of these cysts.
How are pilonidal cysts treated?
Treatment for pilonidal cysts may include draining the cyst, antibiotics to treat infection, and in some cases, surgical removal of the cyst. Keeping the area clean and free of hair may also help prevent recurrence.
Can pilonidal cysts be prevented?
While pilonidal cysts cannot always be prevented, keeping the area clean and free of hair, avoiding prolonged sitting, and maintaining good hygiene practices may help reduce the risk of developing these cysts.