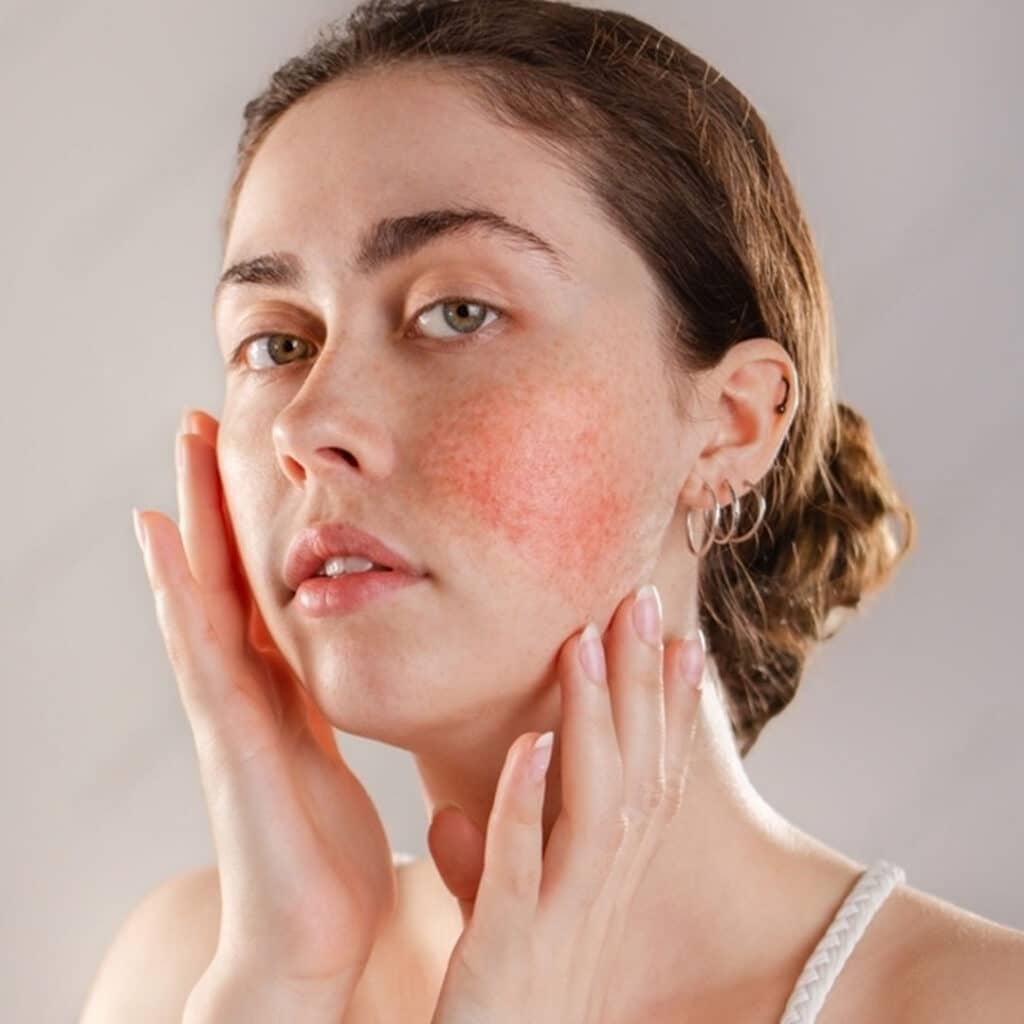
Rosacea Look Like
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the face. It typically affects the central part of the face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. Over time, the redness and flushing can become more persistent and may lead to the development of small, red, pimple-like bumps or pus-filled pimples.
In some cases, rosacea can also cause swelling and thickening of the skin, particularly on the nose, a condition known as rhinophyma. Rosacea can also affect the eyes, causing redness, burning, and itching, a condition known as ocular rosacea.
It is important to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment of rosacea, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other skin conditions, such as acne or skin irritation. Your dermatologist can also recommend a personalized treatment plan to manage your rosacea and improve the appearance of your skin.
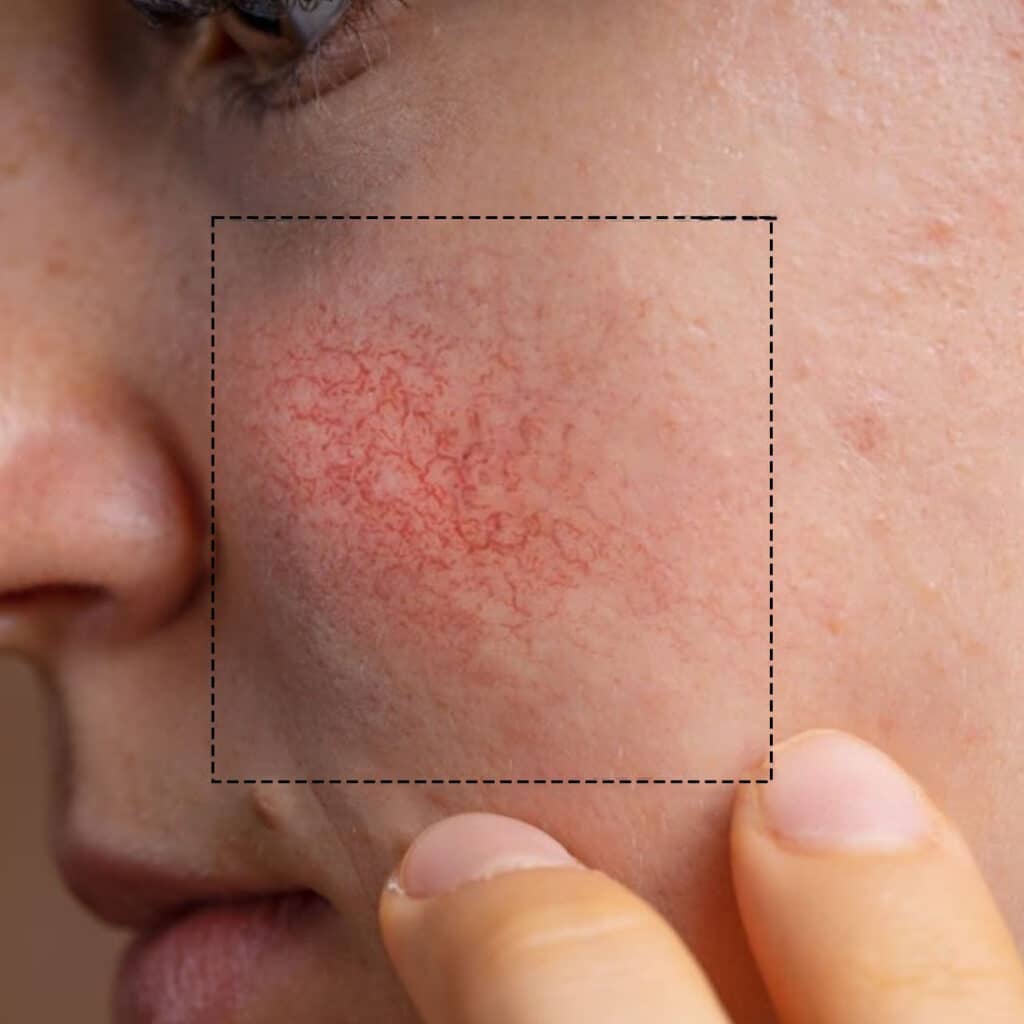
Who gets it, and why?
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can occur in anyone, rosacea is most common in fair-skinned people, particularly those of Celtic or Scandinavian descent. Women are more likely to be affected than men, although the condition may be more severe in men.
The exact cause of rosacea is not known, but several factors are believed to play a role, including:
-
Genetics: Rosacea may be hereditary, as the condition tends to run in families.
Demodex mites: An overpopulation of Demodex mites, which are tiny insects that naturally live on the skin, has been implicated in the development of rosacea.
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation of the blood vessels and skin may play a role in the development of rosacea.
Vascular abnormalities: Abnormalities in the blood vessels of the face may lead to increased blood flow and redness in the skin.
-
Microbes: The presence of certain bacteria, such as H. pylori, and the mite Demodex folliculorum have been linked to rosacea.
Environmental factors: Exposure to sun, wind, heat, and cold, as well as certain foods and drinks, can trigger rosacea in some people.
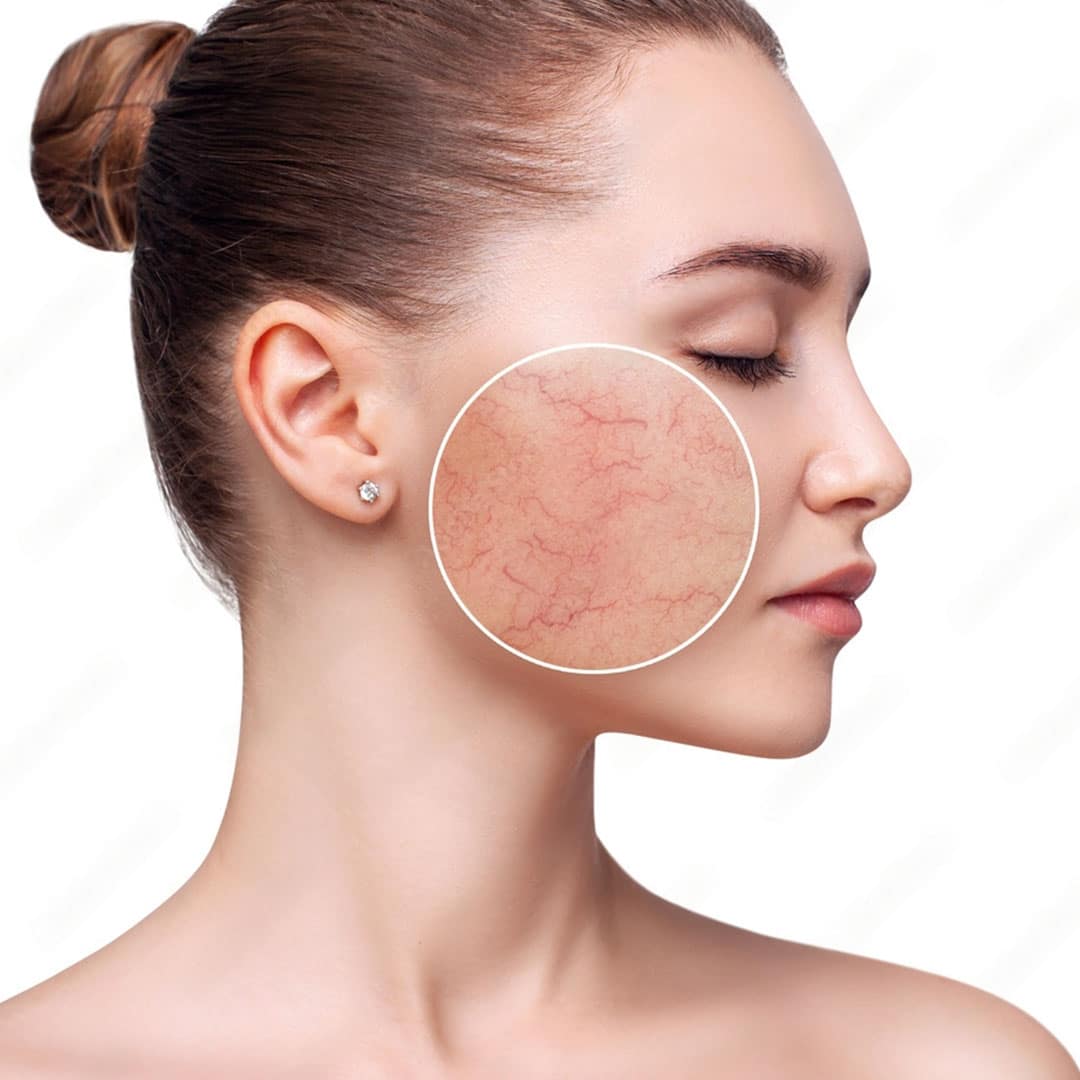
It is important to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment of rosacea, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other skin conditions, such as acne or skin irritation. Your dermatologist can also recommend a personalized treatment plan to manage your rosacea and improve the appearance of your skin.
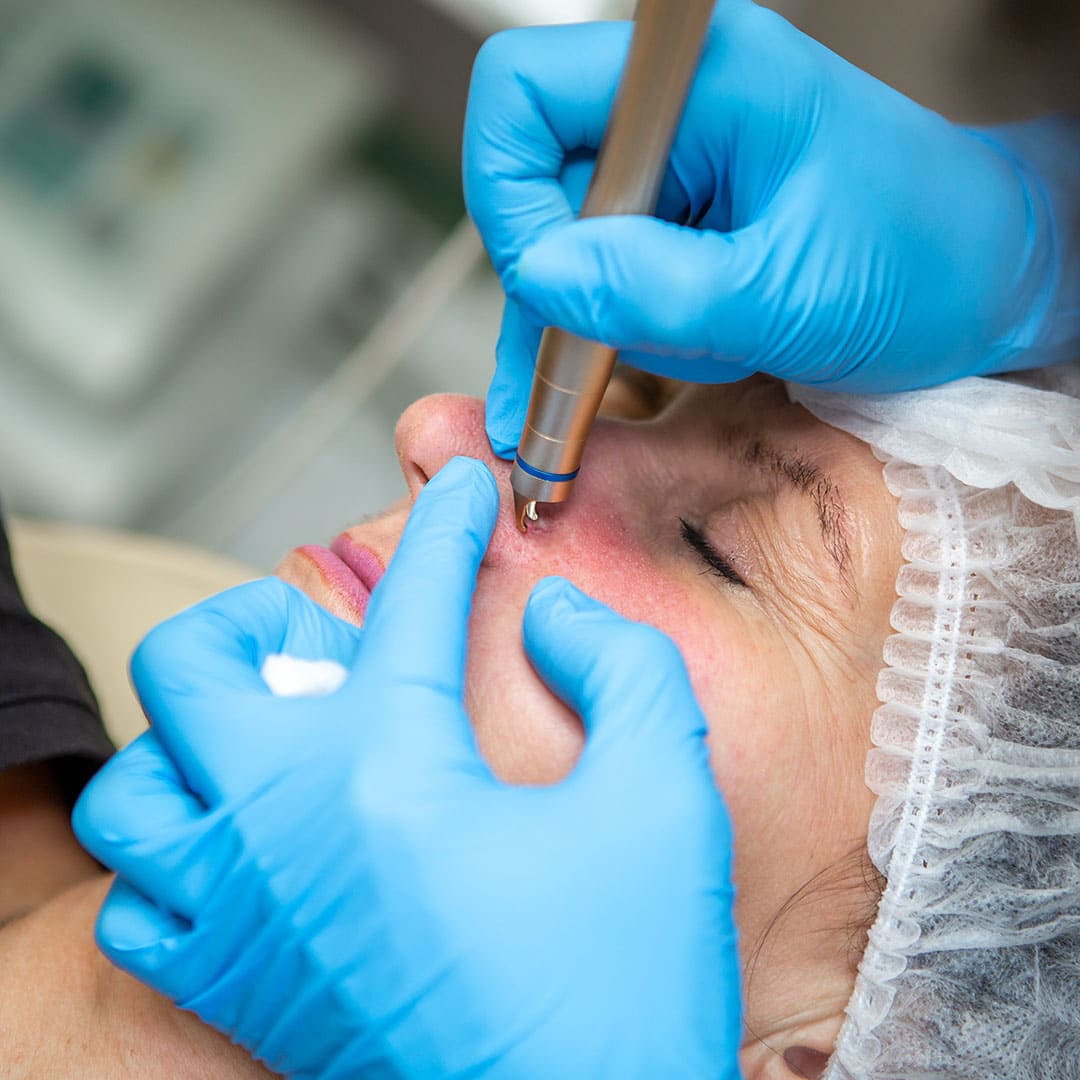
How do you treat Rosacea?
The treatment of rosacea depends on the severity and specific symptoms of the condition. The goal of treatment is to reduce redness and inflammation, as well as to prevent the progression of the condition.
Some of the treatments used to manage rosacea include:
Topical medications: Topical creams, gels, and lotions, such as metronidazole and azelaic acid, can help reduce redness and inflammation and treat pimple-like bumps.
Oral medications: Oral antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, can help reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups of rosacea.
Laser therapy: Certain types of laser therapy, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) and pulsed dye laser (PDL), can help reduce redness and the appearance of blood vessels on the face.
Light-based therapies: Light-based therapies, such as blue light therapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT), can help reduce inflammation and treat pimple-like bumps.
Skin care: A gentle skin care routine, using non-irritating products, can help reduce redness and improve the appearance of the skin.
Avoid triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as sun exposure, alcohol, and spicy foods, can help reduce the frequency and severity of rosacea flare-ups.
It is important to work with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan for rosacea. Your dermatologist can help you choose the best treatments for your specific symptoms and skin type. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be needed to manage the condition effectively.
Some tips for reducing the symptoms of rosacea:
Protect your skin from sun exposure: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and wear a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses to protect your skin from sun exposure.
Avoid triggers: Keep a record of activities or substances that trigger your rosacea flare-ups, and try to avoid these triggers as much as possible. Common triggers include sun exposure, alcohol, spicy foods, and hot drinks.
Use gentle skin care products: Choose non-irritating, fragrance-free skin care products, and avoid using products that contain alcohol, witch hazel, or menthol, as these can be irritating to the skin.
Use cool compresses: Applying cool compresses to the skin can help reduce redness and inflammation.
Avoid hot showers and baths: Hot water can cause skin irritation and increase redness, so opt for lukewarm water instead.
Manage stress: Stress can trigger rosacea flare-ups, so it is important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or counseling.
Seek medical treatment: If you are experiencing symptoms of rosacea, it is important to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.


