Thinning hair can be a distressing experience, affecting not just your appearance but also your self-confidence. For many, it’s a sign of underlying issues, such as hereditary hair loss. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have led to effective solutions.
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that relocates healthy hair follicles to areas where hair is thinning or has been lost. This method offers a permanent solution for individuals experiencing thinning hair, providing natural-looking results that can last a lifetime.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the causes of your hair loss before considering a transplant.
- A hair transplant can restore your hair to its original thickness.
- FUE and FUT are the most popular hair transplant procedures.
- 81.1% of hair transplants are performed on individuals with genetic hair loss.
- A hair transplant offers a permanent solution with lasting results.
Understanding Thinning Hair: Causes and Symptoms
Understanding the causes and symptoms of thinning hair is crucial for determining the best course of treatment. Thinning hair is often confused with hair loss, but they are distinct conditions.
Thinning Hair vs. Hair Loss: What’s the Difference?
Hair thinning refers to a reduction in hair density, whereas hair loss often indicates areas where hair has completely disappeared. For more information on hair loss, you can visit the Mayo Clinic’s website. Understanding this difference is crucial when considering treatment options, as some solutions work better for thinning versus complete loss.
The distinction between thinning hair and hair loss is not just semantic; it has practical implications for treatment. For instance, treatments that promote hair growth may be more effective for thinning hair, while hair loss may require more invasive procedures like hair transplantation.
Common Causes of Hair Thinning
Hair thinning can be caused by various factors, including genetics (male and female pattern baldness), hormonal changes, medical conditions (alopecia areata, androgenic alopecia), stress, nutritional deficiencies, and aging. The progression of hair thinning is typically gradual, starting with reduced hair diameter and density before potentially advancing to more noticeable loss.
| Cause | Description | Impact on Hair |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Inherited traits leading to pattern baldness | Reduced hair density, especially on the scalp |
| Hormonal Changes | Changes in hormone levels affecting hair growth | Thinning of hair, potentially leading to baldness |
| Medical Conditions | Alopecia areata, androgenic alopecia, etc. | Patchy or widespread hair loss |
Common symptoms of thinning hair include a wider part line, more visible scalp, reduced ponytail thickness, and increased hair shedding during washing or brushing.
When to Consider a Hair Transplant for Thinning Hair
A hair transplant can be an effective solution for thinning hair, but timing is everything. Hair transplant procedures are usually suitable for individuals with androgenetic alopecia, a type of genetic hair loss commonly known as male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss.
Hair transplants work when hair is thinning at the root. To determine if you’re a good candidate, it’s essential to understand the causes of your hair loss.
Ideal Candidates for Hair Transplantation
The ideal candidate for a hair transplant typically has stable hair loss that has progressed beyond the early stages but still maintains sufficient donor hair for harvesting. Hair transplants are most effective for those with androgenetic alopecia, which accounts for approximately 80% of all transplant procedures.
- Candidates should be in good overall health and have realistic expectations about results.
- They should understand that the procedure addresses existing hair loss but may not prevent future thinning.
Signs Your Thinning Hair May Benefit from a Transplant
Signs that your thinning hair may benefit from a transplant include noticeable recession at the hairline, thinning at the crown, and hair loss that has stabilized or progressed slowly.
- Those with diffuse thinning throughout the scalp may still be candidates but should undergo thorough evaluation.
- Age is an important consideration, with younger patients advised to wait if their hair loss pattern hasn’t fully established.
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures
There are two primary hair transplant techniques that individuals can consider for addressing thinning hair: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a modern hair transplant method that involves individually extracting hair follicles from the donor area, typically the back and sides of the head, and transplanting them to areas of thinning or balding. This technique leaves minimal scarring and is ideal for patients who prefer to wear their hair short.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and then transplanting these units to the recipient area. While it leaves a linear scar, FUT often allows for harvesting more grafts in a single session and may be more cost-effective.
The choice between FUE and FUT depends on several factors, including the extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, budget considerations, and personal preferences regarding recovery time and scarring. Both procedures have their advantages and are suited to different needs and preferences.
The Hair Transplant Process for Thinning Hair
A hair transplant can offer a permanent solution to thinning hair, but it’s essential to understand the process involved. The procedure is meticulous and requires careful planning and execution to achieve natural-looking results.
Pre-Procedure Consultation and Planning
The hair transplant process begins with a comprehensive consultation where the surgeon evaluates your hair loss pattern, discusses your goals, and determines the appropriate technique for your situation. During this phase, the surgeon will map out the recipient areas and design a natural-looking hairline.
During the Procedure: What to Expect
On the day of the procedure, local anesthesia is administered to both the donor and recipient areas to ensure comfort throughout the surgery. Depending on the chosen technique (FUE or FUT), grafts are harvested and then carefully placed in the recipient areas. The actual transplantation process is time-consuming, often taking 4-8 hours.
Recovery and Initial Results
Immediately after the procedure, your scalp may appear red with small scabs at the transplant sites, which is normal and will heal within 7-10 days. Initial recovery involves following specific post-operative care instructions. Patients typically see initial results within 3-4 months as the transplanted hair begins to grow, with full results becoming visible around 12-18 months post-procedure.
Timing Considerations: When Is the Right Time?
Hair transplant timing is a complex consideration that involves multiple factors, including the extent of hair loss, age, and the stability of the hair loss pattern.
Age and Hair Loss Progression Factors
The decision to undergo a hair transplant is significantly influenced by the patient’s age and the progression rate of their hair loss. Younger patients, typically those under 25, are often advised to wait because their hair loss pattern may not be fully established.
- Assessing the stability of the hair loss pattern is crucial.
- The Norwood Scale for men and Ludwig Scale for women are used to assess hair loss progression.
- Transplants are typically recommended for those at Norwood stage 3+ or advanced Ludwig stage 1.
The Dangers of Getting a Transplant Too Early or Too Late
Getting a transplant too early can lead to an unnatural appearance as the surrounding native hair continues to thin, potentially requiring additional procedures. Conversely, waiting too long may result in extensive donor area depletion, making the procedure more challenging.
The ideal time for a hair transplant often involves a period of stabilization with medical treatments like finasteride or minoxidil before proceeding with surgical intervention. A comprehensive consultation with a hair restoration specialist is essential to determine the right time for the procedure.
Limitations of Hair Transplants for Thinning Hair
Understanding the limitations of hair transplants is crucial for managing expectations. While hair transplant procedures can significantly improve the appearance of thinning hair, they are not without their constraints.
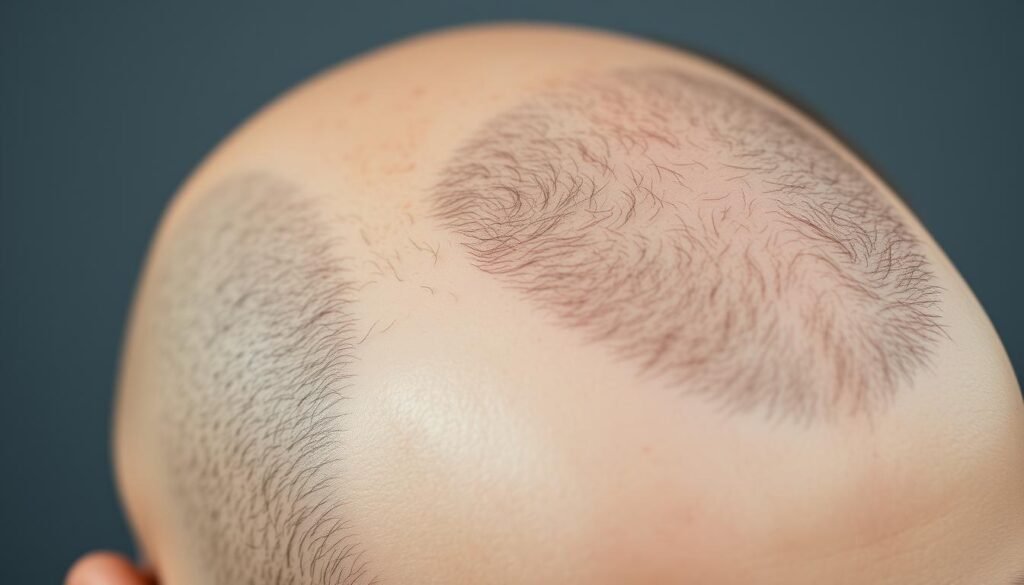
Donor Hair Availability Constraints
The donor area, typically located at the back and sides of the head, contains a finite number of follicles that are resistant to hair loss. The limited availability of donor hair means that there may not be enough grafts to achieve the desired density, particularly for individuals with extensive hair loss across large areas of the scalp.
| Donor Hair Characteristics | Impact on Transplant |
|---|---|
| Thickness | Affects coverage per graft |
| Color | Influences natural appearance |
| Texture | Impacts overall result |
Continued Hair Loss After Transplantation
Another significant limitation is that hair transplants do not halt the progression of genetic hair loss in non-transplanted areas. As a result, native hair may continue to thin, potentially leading to an unnatural appearance over time if not addressed with additional procedures or medical therapy.
“The safe, genetically resistant to hair loss donor area is much smaller than the scalp where hair tends to be lost in male pattern hair loss.”
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Understanding the potential side effects of hair transplant surgery is crucial for making an informed decision. While generally considered safe, hair transplants carry certain risks that patients should be aware of before proceeding.
Short-Term Complications
In the short term, patients may experience complications such as infection at the donor or recipient sites, bleeding, swelling, scalp numbness or pain, and the formation of small cysts around transplanted follicles. Most patients experience some degree of shock loss, where existing hair temporarily falls out due to trauma from the procedure, though this typically resolves within a few months.
Long-Term Considerations
Long-term considerations include the possibility of scarring, particularly with FUT, unnatural-looking results if performed by an inexperienced surgeon, and the need for additional procedures if hair loss continues. In rare cases, patients may experience poor graft survival, where a significant percentage of transplanted follicles fail to grow, necessitating a revision procedure.
To minimize the risk of complications, it’s essential to choose a qualified, experienced surgeon and follow all pre and post-operative care instructions carefully. By doing so, patients can significantly reduce the risk of adverse effects and achieve the desired outcome from their hair transplant.
Alternative Treatments for Thinning Hair
Before opting for a hair transplant, it’s essential to explore the range of alternative treatments for thinning hair. These alternatives can offer less invasive and potentially more cost-effective solutions for individuals experiencing hair loss.
Medication Options: Minoxidil and Finasteride
For men and women experiencing thinning hair, medication can be an effective first line of treatment. Finasteride, known by the brand name Propecia, is an oral medication that inhibits the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss in men. On the other hand, Minoxidil (Rogaine or Regaine) is a topical treatment available for both genders, which works by extending the hair growth phase and increasing blood flow to the scalp.

Non-Surgical Treatments and Emerging Therapies
Beyond medications, there are several non-surgical treatments gaining attention for their potential in addressing thinning hair. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is one such emerging treatment that utilizes the body’s own growth factors to stimulate hair follicles. Additionally, low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices have been shown to promote hair growth with minimal side effects. Cosmetic solutions like scalp micropigmentation and high-quality hair systems can also provide immediate visual improvements for those with early-stage thinning.

It’s worth noting that combination approaches often yield the best results, with many patients using medical therapies alongside surgical options for comprehensive hair restoration. By considering these alternative treatments, individuals can make informed decisions about the most suitable options for their specific needs.
Conclusion: Is a Hair Transplant Right for Your Thinning Hair?
A hair transplant can be a viable option for individuals with thinning hair, but it’s essential to assess your eligibility and the potential outcomes. Consulting with a qualified hair restoration specialist is crucial to determine the best treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
By understanding the causes of your hair loss, evaluating your donor hair availability, and considering your overall health, you can make an informed decision about undergoing a hair transplant. Reviewing before and after photos of previous patients can also provide insight into the potential results you can expect from your procedure.