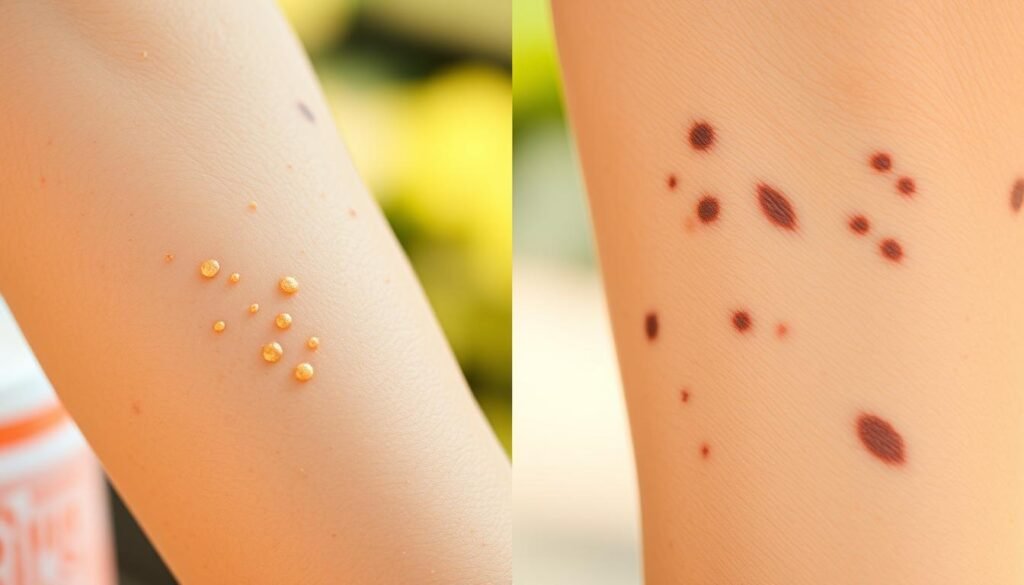
Up to 90% of visible skin aging comes from the sun, says the American Academy of Dermatology. It’s key to know the difference between freckles and sun damage. This knowledge helps you take better care of your skin and catch early warning signs.
This guide will help you understand Freckles vs Sun Damage. We’ll cover how each looks, behaves through the seasons, and when to see a dermatologist. You’ll learn about the size, color, and lasting nature of freckles and age spots. We’ll also point out sun damage symptoms that need attention. Plus, we’ll highlight signs that might indicate skin cancer.
Freckles are usually small and fade when the sun goes away. Sun damage shows up as bigger, more lasting spots. By following simple daily routines like using broad-spectrum SPF, staying in the shade, and doing self-checks, you can protect your skin. This way, you can feel confident about what you see on your skin.
Key Takeaways
- Most visible aging comes from UV exposure, making recognition of Freckles vs Sun Damage essential.
- Freckles are small, often fade in winter; age spots from sun damage are larger and persist.
- The difference between freckles and sun damage includes timing, size, borders, and seasonality.
- Watch for sun damage symptoms like uneven tone, rough texture, and spots that don’t fade.
- Freckles vs skin cancer: any spot that changes in size, shape, color, or bleeds needs a dermatology check.
- Daily prevention—broad-spectrum sunscreen, hats, and shade—reduces risk of freckles vs age spots and long-term photoaging.
Understanding Freckles: Definition and Appearance
Freckles are small, flat spots that appear on sun-exposed skin. They are not raised growths but pigment shifts. Light triggers color changes in freckles, making them more noticeable with the seasons.
Ephelides—the medical term for common freckles—show how skin reacts to UV light. They highlight the mix of genetics and sun damage, affecting freckles from spring to late summer.
What Are Freckles?
Freckles, or ephelides, are small spots that form when sunlight boosts melanin production. They are flat, usually 5 mm or less, and darken with sun and lighten in winter.
People often notice freckles start in childhood. These spots show the skin’s response to UV, linking daily exposure to freckles and sun damage.
Characteristics of Freckles
- Freckles appearance: flat, even edges, darker than nearby skin, not scaly or raised.
- Color range: red, tan, light to dark brown, and nearly black depending on skin tone.
- Seasonal shift: fade in low light months and re-darken with sun.
This definition matches how ephelides act like tiny umbrellas of melanin. Their look changes with UV intensity through the year.
| Feature | Details | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Typically ≤ 5 mm, round to oval | Helps distinguish ephelides from larger lesions |
| Elevation | Flat, not raised | Supports a precise freckles definition |
| Color Behavior | Darkens with sun, lightens in winter | Signals UV-driven change linked to the causes of freckles and sun damage |
| Border | Even, well-defined edges | Part of typical freckles appearance |
| Onset | Often begins in childhood or teen years | Reflects genetic sensitivity to UV |
Common Locations on the Body
Freckles cluster where sunlight hits most. The bridge of the nose, cheeks, shoulders, forearms, and hands are classic sites.
This distribution links what are freckles to day-to-day exposure. It also explains why ephelides intensify on the face and arms during brighter months, tying freckles appearance to the causes of freckles and sun damage across a lifetime.
Understanding Sun Damage: Definition and Appearance
Sun exposure greatly affects how our skin looks and ages. Knowing what sun damage is helps us understand our skin better. This way, we can read our skin’s signals with confidence.
What Is Sun Damage?
Dermatologists call long-term UV impact photoaging. UVA rays go deep and cause lines, laxity, and dark spots. UVB rays cause sunburn.
Together, they lead to solar lentigines that last all year. These spots don’t change much with the seasons. They may even get darker with more sun.
Characteristics of Sun-Damaged Skin
Look for flat, well-defined patches that are darker than the rest of your skin. Age spots are bigger than freckles, up to two centimeters. They can be tan to deep brown.
Sun damage also causes fine lines, a crepey texture, and uneven tone. You might see clusters of solar lentigines with dryness, big pores, and rough patches.
Common Locations on the Body
Sun-exposed areas show changes first. The face, forehead, and temples often get solar lentigines first. Age spots appear on the cheekbones.
The backs of the hands, shoulders, and forearms also show damage. This is from daily driving and being outside. Here, freckles vs age spots is clearer as spots last all year.
Causes of Freckles
Freckles happen when melanin clumps in small spots on the skin. They show how our skin reacts to light and often start in childhood. Even though they show sun exposure, they’re not the same as sun damage.
Genetic Factors
The MC1R gene plays a big role in freckles. Changes in this gene make skin more likely to freckle. This is why freckles often run in families and are more common with red or light hair.
Those without these gene changes might tan or burn but won’t freckle like others. In short, genes set the stage, and light exposure adds the details.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones can also affect how freckles look. Puberty, pregnancy, or birth control changes can darken existing spots. These changes don’t create new freckles but can make existing ones more noticeable.
Dermatologists say this effect is small compared to genetics and sunlight. Yet, it helps explain why freckles change over time.
Environmental Triggers
UV light is a big environmental trigger for freckles. Sun exposure makes freckles more visible in those with the MC1R gene. They often fade in winter and come back with the sun in spring and summer.
This is why some people confuse freckles with sun damage. Freckles are a UV response in certain skin, while damage is deeper. Using sunscreen and managing sun time can reduce these effects.
Causes of Sun Damage
Sun damage happens over time. Even small amounts can add up. Direct sunlight, artificial sources, and daily habits increase exposure. Knowing these causes helps us make better choices to prevent sun damage and freckles.

UV Radiation Exposure
UVA and UVB rays are both harmful. UVA goes deep, causing fine lines, uneven skin tone, and dark spots. UVB burns the skin, leading to redness and peeling.
UV radiation can damage DNA, causing lasting skin changes like solar lentigines. High UV index hours from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. are risky for the face, neck, shoulders, and hands. Protecting during these times helps prevent sun damage.
Tanning Beds and Sunlamps
Indoor devices like tanning beds and sunlamps give intense UVA and UVB. This quick exposure speeds up aging and dark spot formation. The damage from these devices is similar to outdoor sun damage, showing up as stubborn spots.
Using bronzing lotions without UV or makeup with a natural glow is safer than using lamps or beds. These alternatives offer a safer way to get a tan.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to the sun changes with the season, altitude, water, and snow. Sand and water reflect rays, making beach and lake time riskier. Snowfields can double exposure, even on cold days.
Traveling near the equator, working outdoors, and playing sports increase sun exposure. Wearing lightweight clothes, taking shade breaks, and using broad-brim hats from brands like Columbia and Patagonia helps manage these risks. These actions support prevention tips for freckles and sun damage.
Seasonal Changes and Skin Appearance
Skin changes with the seasons. As light and routines shift, so do freckles, tone, and texture. These changes affect how we see new spots and plan our daily care.
How Winter Affects Skin
Cold air and indoor heat dry out the skin. With less UV, winter freckles often fade, but sunspots stay. Dry skin can make spots look sharper, even if the color fades.
Short days mean less UV, but snow glare can cause color in fair skin. A good moisturizer and SPF protect the skin on cold, bright mornings.
Summer’s Impact on Skin
Longer days mean more UV, making freckles darker and spots more visible. Heat and humidity increase oil, which can make skin tone look uneven after being outside.
Being outside without protection can cause lasting damage. Taking shade breaks and reapplying sunscreen helps keep skin safe while enjoying the outdoors.
Seasonal Skin Care Tips
Always use broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours and after swimming or sweating to prevent sun damage.
- Protection: Wear UPF clothing, a wide-brim hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Repair: Add a vitamin C serum in the morning to fight free radicals from UV and pollution.
- Hydration: Switch to a ceramide-rich cream in winter; opt for lighter gels in heat.
- Monitoring: Track seasonal skin changes with monthly photos to spot shifts as winter freckles fade and return with summer sun exposure.
- Smart habits: Apply prevention tips for freckles and sun damage year-round: shade, sunscreen, clothing, and routine check-ins.
Daily Habits Influencing Skin
Small choices can make a big difference on your skin. By following simple daily habits, you can soften the look of freckles and slow down photoaging. A mix of sunscreen, antioxidant skincare, and hydration can help prevent sun damage without adding to your morning routine.
Skincare Routines and Their Effects
Start with a gentle cleanser, then apply a vitamin C serum. Brands like SkinCeuticals or La Roche-Posay are good choices. Finish with a light moisturizer. This step helps protect your skin from free radicals that cause dark spots.
Regular skincare can make your skin look brighter and more even. Over time, it may even soften freckles. Keep a log to track changes and talk to your dermatologist about the best treatments.
Sunscreen and Sun Protection Habits
Use a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher every morning. Reapply every two hours, or after swimming or sweating. Look for lightweight formulas from Neutrogena, Supergoop!, or EltaMD.
Wear a brimmed hat, UV-blocking sunglasses, and UPF clothing for extra protection. Stay in the shade from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. These steps work together with skincare to prevent new spots and support treatments.
Importance of Hydration
Drinking water and using a moisturizer with glycerin or hyaluronic acid makes your skin look smoother. Brands like CeraVe or Eucerin are good choices. This helps keep your skin’s barrier strong and supports repair.
When your skin’s barrier is strong, it can handle skincare products better. This means your daily habits, including sunscreen and skincare, can do more to prevent sun damage and treat freckles and sun damage.
| Habit | Why It Matters | How to Do It | Expected Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning Antioxidant | Neutralizes UV-driven free radicals | Apply vitamin C serum before moisturizer | Brighter tone; fewer new dark spots |
| Broad-Spectrum SPF | Shields UVA/UVB that darken freckles | SPF 30+ daily; reapply every 2 hours | Sun damage prevention; balanced pigment |
| Physical Sun Gear | Adds reliable coverage beyond SPF | Wear hat, sunglasses, UPF clothing | Less cumulative exposure |
| Barrier Hydration | Improves tolerance to actives | Use ceramide or HA moisturizer | Smoother texture; better results |
| Routine Tracking | Links habits to skin changes | Note flare-ups and product use | Informed treatment options for freckles and sun damage |
Recognizing Symptoms of Freckles
Spotting freckles starts with looking at their pattern and where they are. They show up as flat spots on the nose, cheeks, shoulders, and forearms. These spots are harmless and often run in families, linked to certain genes.
Watching how freckles change in size and color is key. This helps you tell if they are freckles or sun damage during regular checks.
Size and Color Variations
Freckles are usually under 5 mm and round with smooth edges. They can be red, tan, light, or dark brown, depending on your skin. Their uniform color and flat surface help tell them apart from other spots.
When checking freckles, notice if their color stays the same. Any sudden change in size, shape, or color is a sign to see a doctor. This is where Freckles vs Sun Damage can get confusing, so compare new spots to old ones.
How Freckles Change with Sun Exposure
Freckles can darken and grow in summer, then fade in winter. This change is because of more sunlight, not because the skin is hurt.
Using sunscreen and hats can help freckles change less over the year. If you want to treat freckles for looks, there are options like tinted sunscreen, vitamin C serums, and laser treatments. These don’t cure disease but can even out your skin tone while you watch for Freckles vs Sun Damage.
| Feature | Typical Freckles | Helpful Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Shape & Elevation | Flat, round or oval; not raised | Flat texture aligns with common freckles symptoms |
| Size | Pinpoint to ≤5 mm | Stable, small spots guide freckles size and color checks |
| Color | Uniform red, tan, brown, or near‑black | Even tone helps distinguish Freckles vs Sun Damage |
| Seasonal Pattern | Darken with sun; fade with less UV | Track how freckles change between summer and winter |
| Common Sites | Face, nose, cheeks, shoulders, forearms | Areas with frequent exposure show clusters first |
| Care Approach | Daily SPF, hats, gentle brighteners | Cosmetic freckles treatment aims for tone balance |
Recognizing Symptoms of Sun Damage
Small changes in your face and hands can show early signs of sun damage. Look for changes that last through winter and compare them to your skin a year ago. This helps you tell the difference between freckles and sun damage.

Signs of Premature Aging
Fine lines around your eyes and mouth can deepen quickly. These are signs of premature aging from UVA rays. In the afternoon, these lines seem deeper, and makeup doesn’t smooth over them.
Look for wide, flat brown patches that don’t fade by spring. These are signs of long-term sun exposure, not just freckles. Tracking these changes helps you know the difference.
Texture Changes in the Skin
Sun damage can make your skin feel rougher. It might feel dry, patchy, or sandpapery, mainly on your temples, cheeks, and hands. Your pores might look bigger, and your skin might lose its glow.
If a spot becomes scaly, thick, or tender, pay attention. Sudden texture changes need a closer look. Keeping a photo log on your phone helps track changes over time.
Color Changes and Uneven Tone
Blotchy patches and shadows on your forehead and cheeks show uneven skin tone. Some areas darken after being outside and stay that way, even with moisturizer. Sunspots can grow and stay visible all year.
Freckles are small and scattered, looking like dust. Sunspots are bigger and clear. Tracking these color changes helps you decide on care and understand the difference between freckles and sun damage.
- Key cue: Spots that darken with more sun yet fail to fade in winter suggest lasting sun damage symptoms.
- Visual check: Mixed tones across the cheeks and temples often signal uneven skin tone, not just freckles.
- Pattern test: Freckles vs age spots becomes clearer when edges look sharp and patches expand beyond a few millimeters.
Situations Where Freckles Become Noticeable
Freckles often show up on the nose, cheeks, shoulders, and forearms, mainly in young people. Their look changes with light, timing, and genetics, making them more visible at different times of the year.
Sun Exposure Duration
Being in direct sunlight makes melanin work harder, making spots darker and freckles more noticeable. Even short times in the sun can make a difference, but longer periods in the midday sun have a bigger impact.
It’s good to take breaks in the shade, wear a wide-brimmed hat from Patagonia, and use Neutrogena’s daily SPF 30. These steps help reduce freckles and sun damage without hiding your natural color.
Seasonal Changes in Sun Intensity
UV rays are strongest from late spring to summer, causing freckles to darken. They lighten when daylight hours get shorter.
In winter, the sun’s rays hit at a lower angle, reducing sun damage. This means many people see their freckles looking lighter. It’s important to keep using SPF and sunglasses from Ray-Ban, even when it’s cooler.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Changes in body chemistry can make freckles more visible during times like adolescence or pregnancy. But, UV rays and genetics are the main reasons for freckles and sun damage.
Keep an eye out for new or changing freckles. Compare them to skin cancer signs using clear photos and dates on your phone. This helps track freckles throughout the seasons.
Situations Where Sun Damage Becomes Noticeable
Changes often start slow and then appear suddenly. Early signs show up on the face, hands, shoulders, and forearms. These areas help you spot the difference between freckles and age spots.
Extended Sun Exposure
Being outside without shade for hours increases damage. UVA and UVB rays cause deeper changes, like fine lines and spots. Over time, spots become more defined, making it easier to tell them apart from freckles.
High UV times, like late morning to midafternoon, are risky. Beach days, sports, and long drives increase damage on the temples, cheeks, and hands.
Skin Care Negligence
Not using SPF or forgetting to reapply leads to neglect. Missed spots often appear first on the hairline, ears, and neck. Not using antioxidants and moisturizers makes changes more noticeable.
Simple steps can help: use daily SPF 30+, wear long sleeves, and use sunglasses. These actions prevent new spots and help maintain an even skin tone.
Age and Skin Type Considerations
With age, photoaging becomes more visible in lighter skin. But, all skin tones can develop dark patches in exposed areas. Oilier skin might hide changes early, while dry skin shows lines faster.
Genetics and melanin levels affect how freckles and age spots appear. Consistent care and smart shade choices help prevent damage across all skin types.
Professional Advice and Diagnosis
Getting a plan starts with a visit to a dermatologist and regular skin checks. These visits help figure out if spots are freckles or skin cancer. They also guide how to monitor your skin at home and find the right treatment for freckles and sun damage.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
See a dermatologist if a spot gets darker, grows, or changes shape. If it starts itching, bleeding, or changing fast, get it checked right away. People with certain freckles or a family history of melanoma should get yearly skin checks.
For peace of mind, get annual skin cancer exams. This makes it easier to tell if spots are harmless freckles or need treatment.
Important Diagnostic Tools
Dermatology clinics use special tools during a dermatologist visit. They start with a clinical exam and dermoscopy to look at the spot’s color and shape. These tools help figure out if a spot is safe or might be cancer.
- Dermoscopy: Magnified, polarized view to analyze color networks and structure.
- Clinical photography: Tracks change over time during routine skin checks.
- Biopsy when indicated: Confirms diagnosis to guide treatment options for freckles and sun damage.
Differences Between Freckles and Sun Damage
Freckles are small, even, and fade with less sun. Sun damage spots are bigger, have uneven color, and stay the same all year. Knowing these differences helps make safer choices when thinking about freckles vs skin cancer.
| Feature | Freckles (Ephelides) | Sun Damage Spots (Solar Lentigines) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Size | Pinpoint to a few millimeters | About 0.5–2.0 cm |
| Color Pattern | Uniform light to medium brown | Darker, variegated or uneven tone |
| Seasonal Behavior | Darken in summer, fade in winter | Persist year-round |
| Onset | Common in youth | More common with age and UV exposure |
| Risk Consideration | Usually harmless; monitor for change | Marker of cumulative UV; evaluate for atypia |
| Next Steps | Sun protection; periodic skin checks | Dermatologist consultation and possible dermoscopy |
| Care Pathways | Cosmetic lightening if desired | Treatment options for freckles and sun damage such as topical retinoids, chemical peels, or laser based on clinical judgment |
If any spot looks new, different, or changing, schedule a professional review without delay.
Summary of Key Differences
Use this summary freckles vs sun damage to understand your skin better. Freckles come from genetics and sun, often linked to MC1R. They are small, even, and change with light.
Sun damage spots, or sunspots, are caused by UV rays over time. They are bigger and stay the same, even when sun exposure goes down.
Quick Reference Comparison
Here’s a quick guide: freckles are tiny dots, usually less than 0.5 cm, and the same color. They fade in winter but get darker in summer. Sunspots are bigger, with deeper, irregular edges and colors.
Freckles show up early in life. Sun damage spots appear later, mainly on the face, hands, arms, and shoulders. They stay even when sun exposure drops.
Importance of Skin Care Awareness
People who freckle easily face a higher skin cancer risk. They should watch their skin closely. Get annual checks from a board-certified dermatologist, do self-exams monthly, and take photos to track changes.
This helps you act fast and choose the right care. It’s a way to stay aware of your skin health.
Prevention Strategies for Healthy Skin
Every day, focus on preventing sun damage. Use broad-spectrum SPF and reapply every two hours. Wear protective clothing, a wide-brim hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Stay in the shade from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Use antioxidants like vitamin C serums to defend your skin. Stay hydrated and use gentle skincare to keep your skin barrier strong. If spots don’t go away, try treatments like IPL or BBL, HALO laser, microneedling, chemical peels, or laser resurfacing. These treatments often need to be done in a series for best results.
Remember, these tips are general advice. They are not meant to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always talk to a doctor before changing your skincare or health routine.