Losing hair can be a distressing experience, affecting not just our appearance but also our self-esteem. It’s normal to shed some hair daily, but excessive loss can be alarming.
Dermatologists are experts in skin and its structures, including hair and scalp. They can diagnose the root cause of hair loss and recommend effective treatment options.
Many people are unaware that a dermatologist can provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment for hair loss. If you’re experiencing excessive shedding, consulting a dermatologist can be the first step towards finding a solution.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss affects millions of Americans, impacting self-esteem and quality of life.
- Excessive or sudden hair loss may indicate an underlying condition requiring professional attention.
- Dermatologists are trained to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the skin, hair, and nails.
- A dermatologist can provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment options for hair loss.
- Seeking professional help is crucial for addressing hair loss concerns.
Understanding Hair Loss: Normal vs. Problematic
The line between normal hair loss and a condition that requires medical attention can be blurry, but understanding the hair growth cycle can help clarify it. Each hair follicle on our scalp is going through a different stage of growth at any given time.
The Natural Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle consists of four phases: anagen, catagen, telogen, and exogen. The anagen phase is the active growth period, lasting from 2 to 7 years, during which the hair grows. The catagen phase is a short transitional period where the follicles shrink, followed by the telogen phase, a resting period that lasts several months. Finally, the exogen phase involves the shedding of the hair strand, making way for new hair growth.
When Hair Loss Becomes Concerning
Hair loss becomes a concern when it’s excessive or accompanied by other symptoms. Normal hair loss involves shedding between 50 to 300 hairs daily, with new hair growth replacing what’s lost. However, if you notice sudden increased shedding, visible thinning, bald patches, or a receding hairline, it may indicate a more serious issue, medically referred to as alopecia. Other warning signs include scalp abnormalities like redness, scaling, or pain, and hair loss accompanied by symptoms such as fatigue or weight changes.
Understanding these signs can help you identify whether your hair loss is normal or if it’s a type of alopecia that requires professional attention.
Do Dermatologists Treat Hair Loss?
For those experiencing hair loss, understanding the role of dermatologists in diagnosis and treatment is essential. Over 55 million Americans suffer from some degree of hair loss, making it a significant concern.
Dermatologists as Hair and Scalp Specialists
Dermatologists are the primary medical specialists who diagnose and treat hair loss conditions. They receive specialized training in disorders affecting the skin, scalp, and hair follicles. This expertise allows them to identify underlying causes that might be missed by general practitioners.
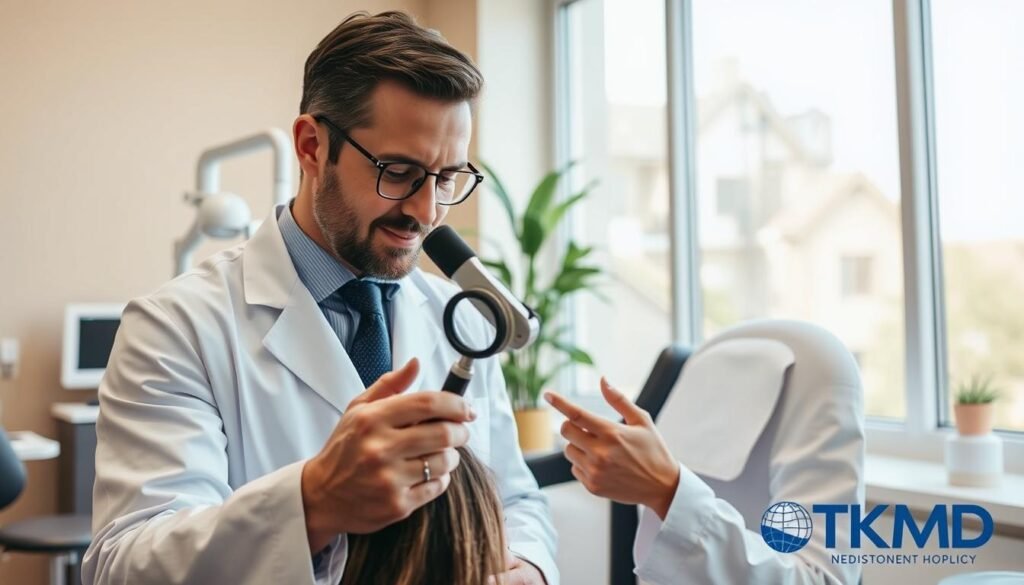

The Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process involves a comprehensive approach, including evaluating medical history, performing physical examinations, and sometimes conducting scalp biopsies. This thorough evaluation enables dermatologists to determine the exact type of hair loss and recommend appropriate treatment.
| Diagnostic Steps | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Medical History Evaluation | Identify underlying health conditions |
| Physical Examination | Assess scalp and hair follicle health |
| Scalp Biopsy | Determine the exact cause of hair loss |
Common Types of Hair Loss Conditions
Understanding the different types of hair loss is crucial for effective treatment. Hair loss, or alopecia, can be caused by a variety of factors, leading to different conditions that affect men and women in distinct ways.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most prevalent form of hair loss affecting over 50% of men over age 50 and many women after menopause. In men, it typically presents as a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while women usually experience diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing well-defined, often circular patches of complete hair loss that can appear suddenly and may affect any hair-bearing area of the body. This condition targets hair follicles, leading to significant hair loss.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss triggered by physical or emotional stress, medications, or hormonal changes, causing excessive shedding throughout the scalp as hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase.
Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia encompasses several inflammatory conditions that destroy hair follicles and replace them with scar tissue, leading to permanent hair loss if not treated promptly.
| Condition | Characteristics | Affected Population |
|---|---|---|
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Receding hairline, thinning at crown | Men over 50, post-menopausal women |
| Alopecia Areata | Circular patches of hair loss | Any age, both men and women |
| Telogen Effluvium | Excessive shedding | Individuals under stress or hormonal changes |
| Scarring Alopecia | Permanent hair loss due to scarring | Any age, both men and women |
Each type of hair loss requires different treatment approaches, making accurate diagnosis by a dermatologist essential for effective management and potential reversal of the condition.
Causes Behind Different Hair Loss Conditions
The causes of hair loss are diverse, ranging from medical conditions to hairstyling practices. Understanding these causes is essential for determining the appropriate treatment.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in androgenetic alopecia, also known as male and female pattern baldness. Multiple genes from both parents influence hair follicle sensitivity to hormones, determining the pattern and age of onset of hair loss. For more information on hair and scalp conditions, visit this resource.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes can significantly impact hair growth. Conditions such as thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and the natural hormonal shifts during menopause or andropause can lead to hair loss. Hormonal imbalances are a key cause of hair loss in both men and women.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Various medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and scalp infections, can trigger hair loss. Additionally, certain medications such as chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, and hormonal treatments can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle factors such as chronic stress, crash dieting, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the hair growth cycle and exacerbate existing hair loss conditions. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preventing hair loss.
Hairstyling Practices and Traction Alopecia
Hairstyling practices that involve tension on the hair follicles, such as tight ponytails or braids, can cause traction alopecia. Frequent use of heat styling tools and harsh hair products can also damage hair and contribute to breakage and thinning.
| Cause | Description | Impact on Hair |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Influence hair follicle sensitivity to hormones | Pattern and age of onset of hair loss |
| Hormonal Imbalances | Changes in hormone levels | Hair thinning or loss |
| Medical Conditions and Medications | Autoimmune diseases, nutritional deficiencies, certain medications | Triggering or exacerbating hair loss |
| Lifestyle and Environmental Factors | Chronic stress, dieting, smoking, alcohol consumption | Disrupting hair growth cycle |
| Hairstyling Practices | Tension on hair follicles, heat styling, harsh products | Causes traction alopecia, breakage, and thinning |
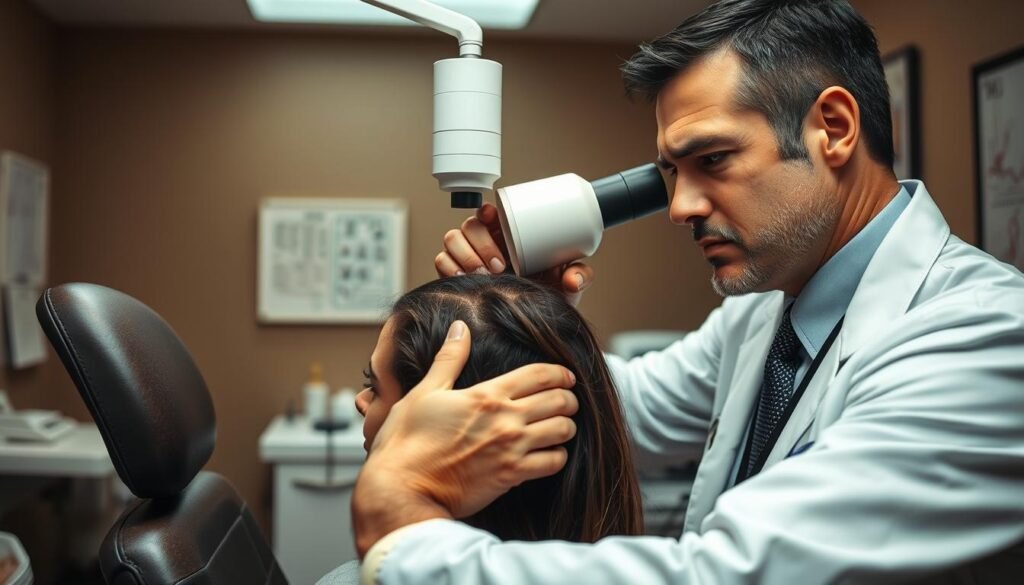
How Dermatologists Diagnose Hair Loss
Dermatologists employ a systematic method to diagnose hair loss, starting with a thorough examination. Diagnosing the underlying cause of hair loss is crucial for effective treatment.
Physical Examination
A comprehensive physical examination of the scalp is essential. Dermatologists assess hair density, pattern of loss, and presence of inflammation or scarring. They also examine the hair shaft quality and look for miniaturization of follicles.
Medical History Assessment
A thorough history assessment is vital. Dermatologists inquire about family history of hair disorders, recent illnesses, medication use, and dietary habits. For women, they also ask about menstrual cycles and hormone therapy, as these factors can influence hair loss.
Laboratory Tests and Scalp Biopsies
Blood tests and scalp biopsies may be necessary to determine the underlying cause. Laboratory tests can include complete blood count, thyroid function tests, and autoimmune markers. A scalp biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin for microscopic examination to aid in diagnosis.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Information Gained |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assessment of scalp, hair density, and pattern of loss | Presence of inflammation, scarring, or miniaturization of follicles |
| Medical History | Family history, recent illnesses, medication use, dietary habits | Underlying causes such as genetic factors, hormonal imbalances |
| Laboratory Tests | Blood tests, scalp biopsies | Systemic conditions contributing to hair loss, presence of inflammation or scarring |
For more information on diagnosing and treating hair loss, you can visit the American Academy of Dermatology or a dermatology specialist’s website.
Treatment Options Provided by Dermatologists
The approach to treating hair loss involves a combination of medical and advanced therapies, as recommended by dermatologists. A treatment plan to get your hair growing again may include one or more of the following: medication, either topical or oral, laser treatment, or surgical procedures like hair restoration or transplantation.
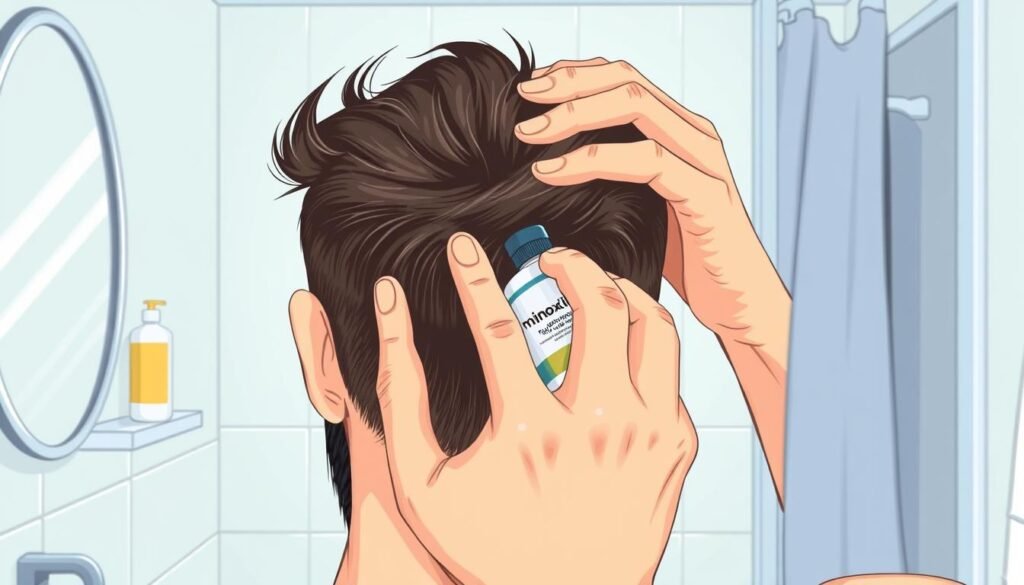
Topical Medications
Minoxidil, commonly known as Rogaine, is a widely used FDA-approved topical medication that helps with hair growth and thickness by prolonging the growth phase of hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp.

Oral Medications
Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication prescribed for male pattern baldness. It works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone involved in hair loss.
Corticosteroid Treatments
Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in conditions like alopecia areata. They can be administered topically, injected directly into the scalp, or taken orally.
Advanced Therapies
Advanced therapies include Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, low-level laser therapy, and Kerafactor. PRP therapy uses growth factors from your own blood to stimulate hair follicles.
Surgical Options for Hair Restoration
For patients with significant hair loss, surgical options like follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) involve relocating healthy hair follicles from donor areas to balding regions.
When to See a Dermatologist for Hair Loss
Determining when to see a dermatologist for hair loss is essential for addressing the issue promptly and effectively. Hair loss can be caused by a variety of factors, and a dermatologist is best equipped to diagnose and treat the underlying condition.
Warning Signs That Require Professional Attention
You should consult a dermatologist if you experience sudden or significant hair loss, noticeable thinning, bald patches, or if your hair doesn’t regrow in areas where it has fallen out. Other warning signs include scalp abnormalities such as redness, scaling, itching, burning, or pain.
- Scalp abnormalities (redness, scaling, itching, burning, or pain)
- Hair loss accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue or unexplained weight changes
- A family history of permanent baldness
What to Expect at Your First Appointment
At your first appointment, expect a comprehensive evaluation including a detailed medical history review and a thorough examination of your scalp and hair. The dermatologist may use a dermatoscope to closely examine hair follicles and scalp condition.
- A detailed medical history review covering medications, recent illnesses, diet, stress levels, and family history of hair disorders
- Blood tests to check hormone levels, nutritional status, or autoimmune markers
- A scalp biopsy if necessary to confirm the diagnosis
Conclusion
Dermatologists are key specialists in diagnosing and treating various forms of hair loss, offering evidence-based treatments and care. Early intervention can prevent progression and improve treatment effectiveness. For comprehensive care, consulting a dermatologist is essential for hair health and overall skin health.


